In this second article of our series, “Lessons Learned from the Recent Rate Hikes and Banking Turmoil,” we’re sharing insights from many years of managing balance sheet and interest rate risk in community banking as members and chairpersons of bank Asset/Liability Management Committees (ALCO).
It’s our belief that a disciplined approach starts with engaging the right people within the organization, establishing confidence in the modeling process, and having a clear understanding of the company’s risk appetite and long-term strategic vision.
Disciplined interest rate risk management in today's complex financial environment is no longer just a best practice; it's a fundamental necessity for navigating the intricate labyrinth of risks and safeguarding organizational stability and profitability.
Banking executives were reminded of the critical importance of disciplined interest rate risk management with the collapse of Silicon Valley Bank, which was primarily attributed to a lack of robust interest rate risk management practices. As the bank failed to effectively anticipate and respond to interest rate shifts, it underscored the necessity for all financial institutions to have a rigorous and adaptive framework for managing interest rate risk. The lessons highlighted potential consequences of neglecting this fundamental aspect of banking and have motivated a renewed focus on interest rate risk management across the sector.
In this article, we hope to give banking executives ideas to consider as they foster a holistic and proactive approach to interest rate risk management.
Create A Collaborative Approach Among ALCO Leadership
Central to our strategy is the establishment of a knowledgeable and experienced ALCO. Comprising senior leaders representing all facets of the balance sheet — loans, deposits, Treasury, credit, and capital — ALCO stands as the bedrock of our interest rate risk management efforts.
However, ALCO cannot function alone. A collaborative and inclusive approach demands input from the Board of Directors, providing valuable strategic insights, education, and awareness. Additionally, the Risk Management Committee's role helps to reinforce ALCO's process, linking it to the broader risk management framework of the organization.
Establish A Robust Asset Liability Management (ALM) Policy
ALCO's key responsibility is the development and maintenance of a comprehensive ALM policy. This policy must align management practices with the bank’s risk appetite and regulatory compliance. A well-constructed policy serves as a compass, guiding operations and ensuring adherence to established risk parameters.
ALCO should complete a thorough review of the bank’s ALM policy following the recent bank failures and rapid rise in interest rates to address potential changes in risk management. Management should re-evaluate with heightened degree of scrutiny, metrics, limits and processes related to rate shocks, derivatives, wholesale funding, deposit concentrations, uninsured deposits, non-maturity deposit decay rates and trends, prepayment assumptions, and capital stress testing.
Build A Disciplined Approach To Pricing
A critical component of the ALM process is a well-defined pricing structure for new loans and deposits. The active and frequent involvement of the loan and deposit pricing teams in this process guarantees dynamic and competitive pricing models that reflect current market conditions, the incremental funding curve, profitability targets, and organizational strategy.
Align With Strategic Planning
Interest rate risk management is not a static process, and neither should be your approach to it. We must implement, and overlay with the ALM process, a comprehensive forecasting process, updated regularly, to capture both your bank’s long-term strategic objectives and near-term changes to balance sheet growth and mix trends.
Stay Current With ALM Strategies And Techniques
In our rapidly changing financial landscape, keeping abreast of regulatory changes, hot buttons, and industry trends is a necessity. Active participation in conferences, webinars, engagement with peer banks, and partnering with a consultant provides valuable insight into industry best practices and potential future challenges.
Implement A Flexible ALM Model
Your ALM model must be agile enough to accommodate the complexities of your balance sheet, incorporate new strategies, multiple rate shocks and derivatives, and provide meaningful output for decision-making. It should fulfill regulatory requirements, align with policy limits, and enable your team to make well-informed decisions that drive your bank forward.
Manage A Conservative Gap
Another priority is conservatively managing your interest sensitivity gap position. Identifying both short-term and long-term exposures to interest rates along the maturity timeline and strategizing to neutralize these exposures is a key component of the risk management process. Tools like brokered deposits and Federal Home Loan Bank advances to match fund long-term fixed rate loan maturities, back-to-back commercial loan interest rate swap program to increase asset sensitivity or a cash flow hedge to extend short-term funding, can help you in this effort.
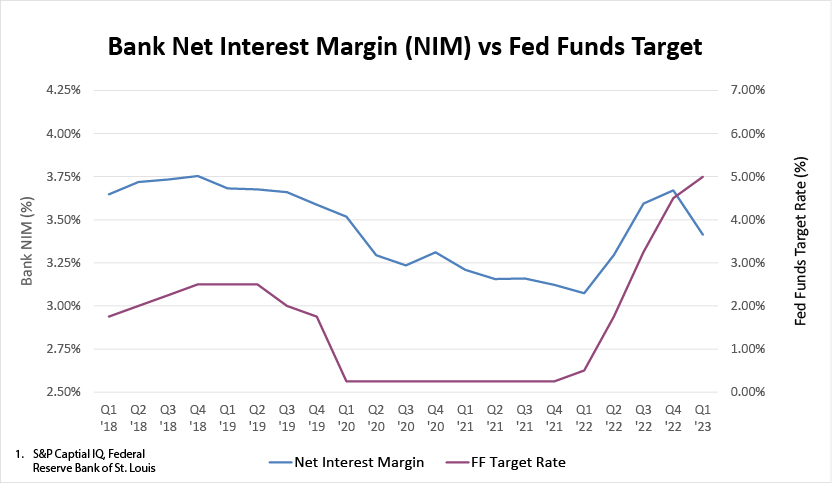
After the height of the COVID-19 pandemic, the Fed raised interest rates 10 consecutive meetings by a cumulative 500 basis points, the most rapid series of increases since the 1980’s. This rapid rise in rates triggered a dangerous mismatch between some banks’ assets paying low rates and liabilities paying high rates.
Embed Stress Testing
While modeling various rate scenarios is critical, it’s equally important to stress these models. Stress testing under extreme but plausible scenarios offers a deeper understanding of your risk profile. It is essential to model multiple rate shocks and twists and assess their impact on Net Interest Margin, Economic Value of Equity, capital planning, and derivatives. We expect greater regulatory scrutiny in this area due to the recent bank failures and interest rate environment.
Understand The Composition Of Non-Maturity Deposits
A comprehensive risk management plan also requires a deep dive into non-maturity deposit characteristics. Pay particular attention to uninsured deposits and large depositor concentrations. It’s vital to also re-evaluate non-maturity deposit decay rates and deposit betas in the current environment to ensure your assumptions are aligned with reality. The non-maturity deposit outflows stemming from the bank failures have prompted banks to re-evaluate the benefits of wholesale funding, such as brokered deposits, which provide a greater degree of certainty for managing liquidity and interest sensitivity than a money market account.
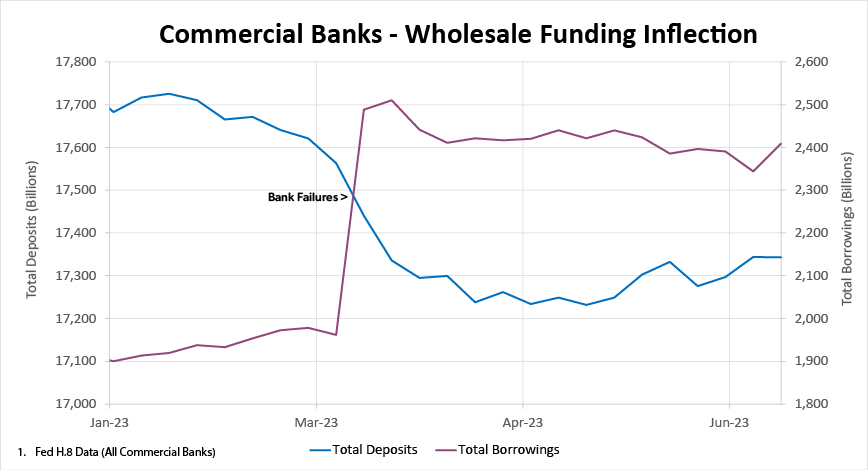
Some of the future challenges to consider as deposit outflows resulting from the bank failures earlier in the year continue to moderate include 1) reliance on wholesale funding is costly, 2) deposit betas may continue to rise as depositors seek attractively-priced alternatives, 3) net interest margins will remain under pressure as incremental cost of funding continues to increase.
Evaluate New Products And Mix
We recommend continually assessing and reconsidering the composition of your loan and deposit portfolios. Exploring the introduction of new products and altering the mix of products can offer opportunities to better match assets and liabilities and increase competitiveness in the market. ALCO should carefully evaluate how such products fit into organizational risk, the regulatory landscape, and how they may react to rapidly changing economic conditions.
Test Internal Controls
A robust interest rate risk management framework also requires a system of strong internal controls and a rigorous audit mechanism. This ensures that the practices and processes are effectively adhering to the ALM policy and highlights any areas that may need tightening or revision. Back testing your model is also an essential element of a strong internal control process and provides ALCO and regulators confidence in model results.
Cultivate A Risk Awareness Culture
Finally, we find that it’s important to incorporate ongoing continuing education and cultivate a culture of risk awareness throughout the bank. Every team member, from junior staff to the board of directors, should understand the importance of disciplined interest rate risk management. A strong risk culture helps ensure that risk management practices are not just followed but valued and integrated into your day-to-day operations.
Disciplined interest rate risk management is a multi-faceted, continuous process that requires the active engagement and collaboration of all banking executives. As leaders, it's our responsibility to spearhead this approach, aligning our teams, policies, and practices towards managing and mitigating interest rate risks effectively. By embracing this disciplined approach, we can navigate the complex world of financial risks and guide our organizations towards a sustainable and profitable future.





